AI Models Are Scaling Rapidly
In 1952, Arthur Samuel created what is widely considered to be the first ever machine learning model. It was a checkers-playing program, which at the time only had a few dozen parameters (tunable weights). Fast forward to today, and many frontier AI models are trained with trillions of parameters. A large portion of this growth can be attributed to the period post-2012, which is referred to as the “Deep Learning Era”. Over the past decade-plus, AI has scaled at a breathtaking pace, and models have become exponentially larger, more computationally intensive, and more efficient.
Here are 6 charts that reveal the staggering growth of AI models:
1) AI Models Are Getting Bigger, and Exponentially More Complex.
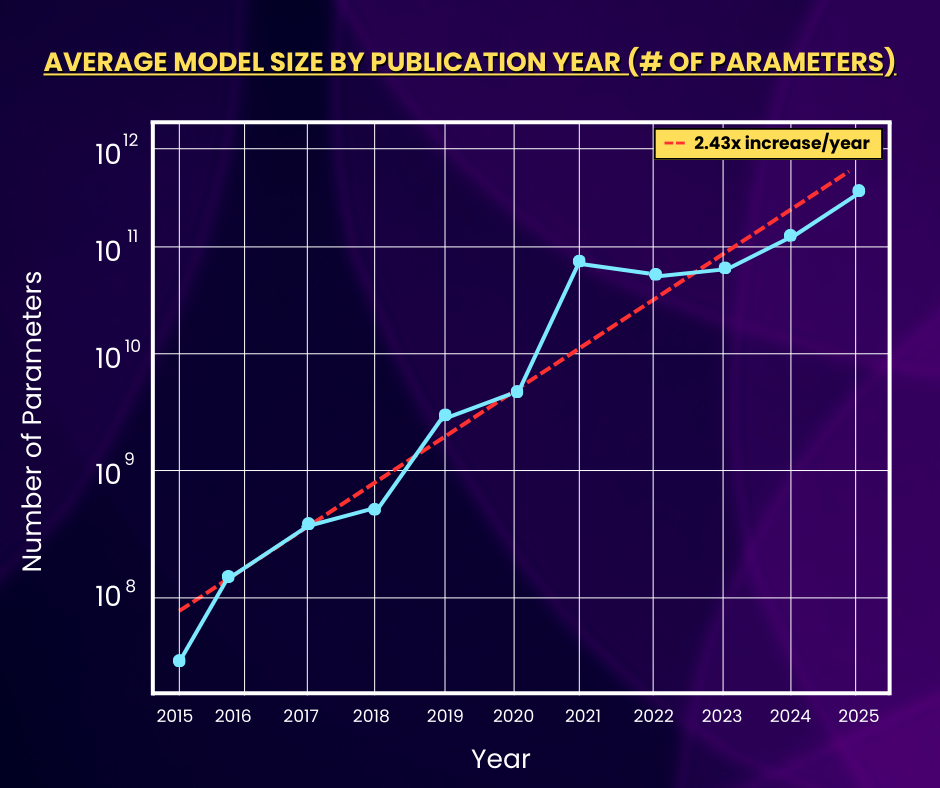
The line graph above shows the average number of model parameters by year over the past decade. Since 2015, the average number of parameters has increased by nearly 4 orders of magnitude, at an exponential rate of 2.43x/year. This is significant because more parameters means greater model complexity, highlighting that models are quickly becoming more and more nuanced in their evaluations.
2) Multimodal Models Are the Next Big Thing.
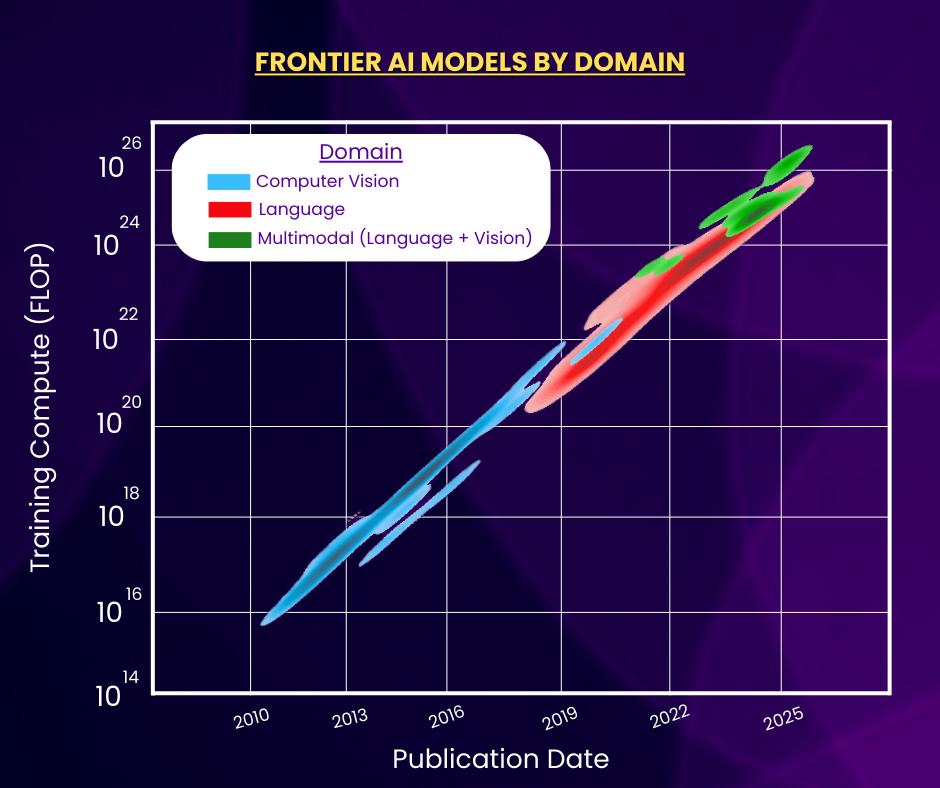
The density plot above shows the publication dates and training computes of frontier AI models grouped into three domains: Vision, Language, and Multimodal. Here, we define “frontier models” as models that were in the Top 10 in training compute when they were released. From the graph, vision models dominated in the early-to-mid 2010s, while language models started taking over in the late 2010s. Then, over the past few years, multimodal models, models that combine language, vision, and other capabilities, have become most prevalent, and will continue to be for the foreseeable future.
3) The Hardware Behind AI Models is Improving Exponentially.
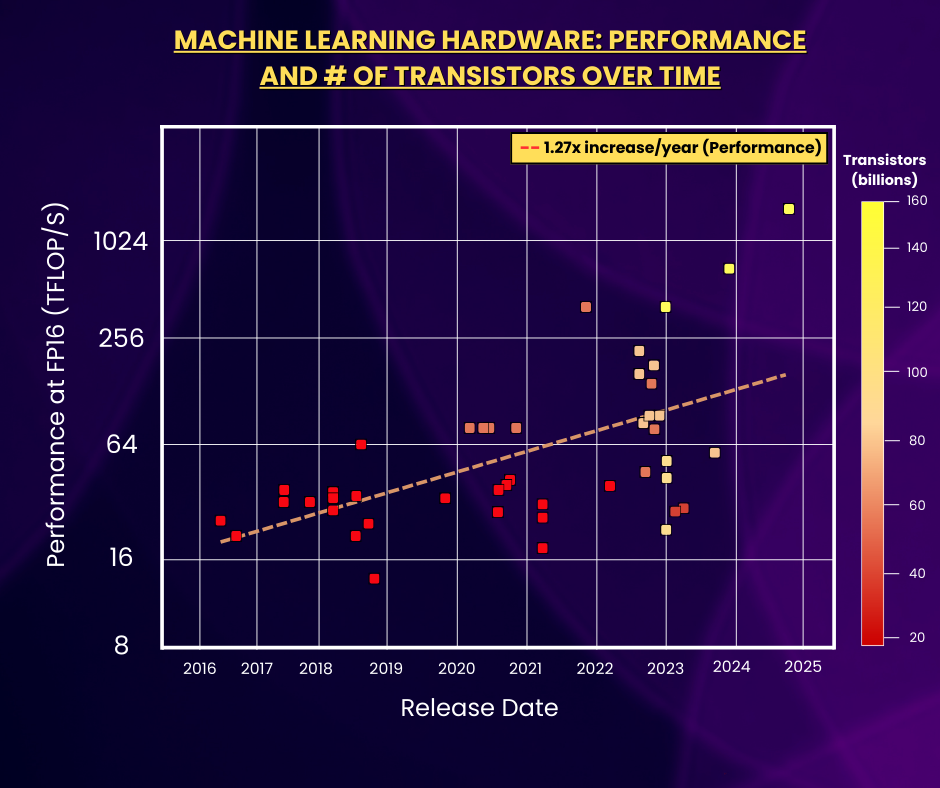
The 3D scatter plot above highlights the growth of ML hardware in terms of both performance and number of transistors over time. Over the past decade, hardware performance has increased exponentially at an average rate of 1.27x/year. Additionally, since 2016, the number of transistors on ML hardware has increased almost 8-fold, from around 20 billion transistors in 2016 to 153 billion transistors for the most recent release in October 2024.
4) AI Model Infrastructure Has Become More Cost-Efficient.
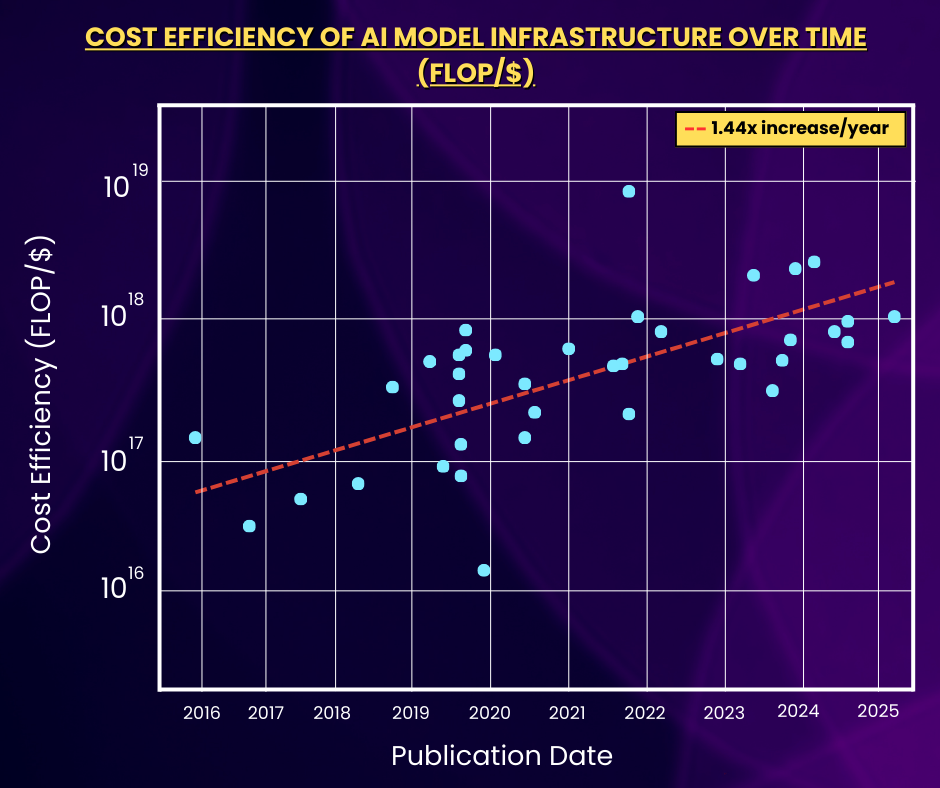
The scatter plot above depicts training cost efficiency for frontier AI models over the past decade. Cost efficiency is measured using the training compute to cost ratio, which is in FLOP (Floating Point Operations) per USD. Based on the regression line, AI model infrastructure has become more cost-efficient by an average multiplier of 1.44x/year, meaning that cost-efficiency has increased by several orders of magnitude compared to 10 years ago.
5) AI Model Infrastructure Has Become More Power-Efficient.
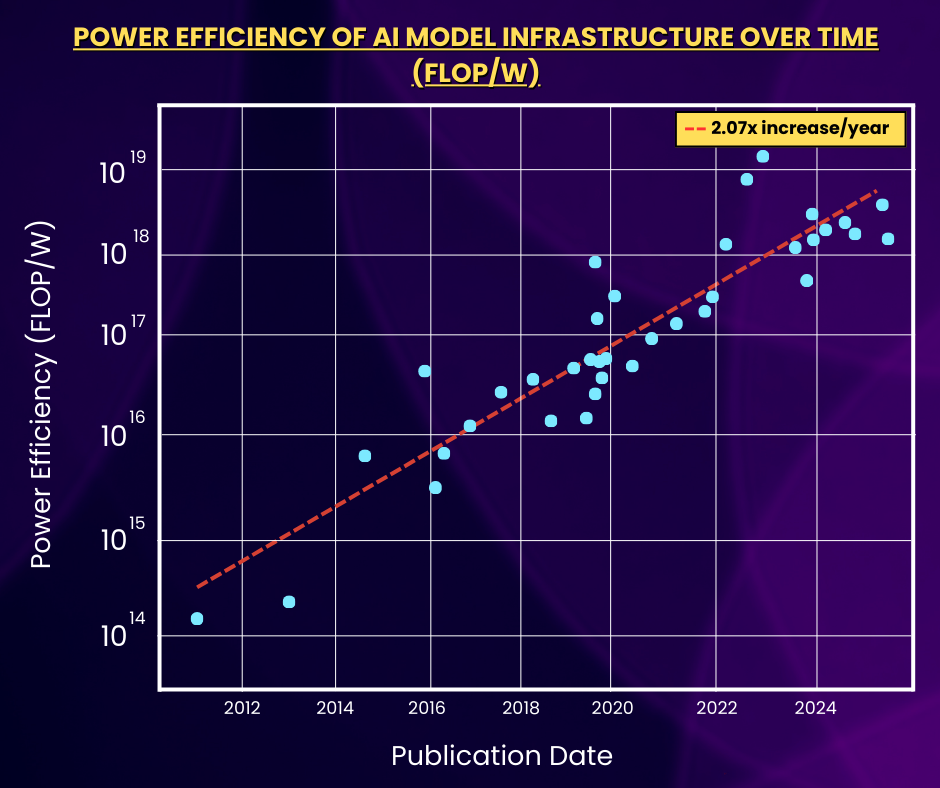
This scatter plot above is very similar to the previous example, but this one depicts power efficiency in terms of FLOP per Watt for frontier AI models. Since 2012, power efficiency has more than doubled every year, meaning that today’s ML hardware can deliver over a thousand times more compute per Watt compared to a decade ago. Yes, the environmental impact of AI is undoubtedly still a concern, but progress in power efficiency gives us hope that models can continue scaling whilst also improving in terms of environmental sustainability.
6) AI Agents Are Advancing: ML Models Are Growing More Agent-Like.
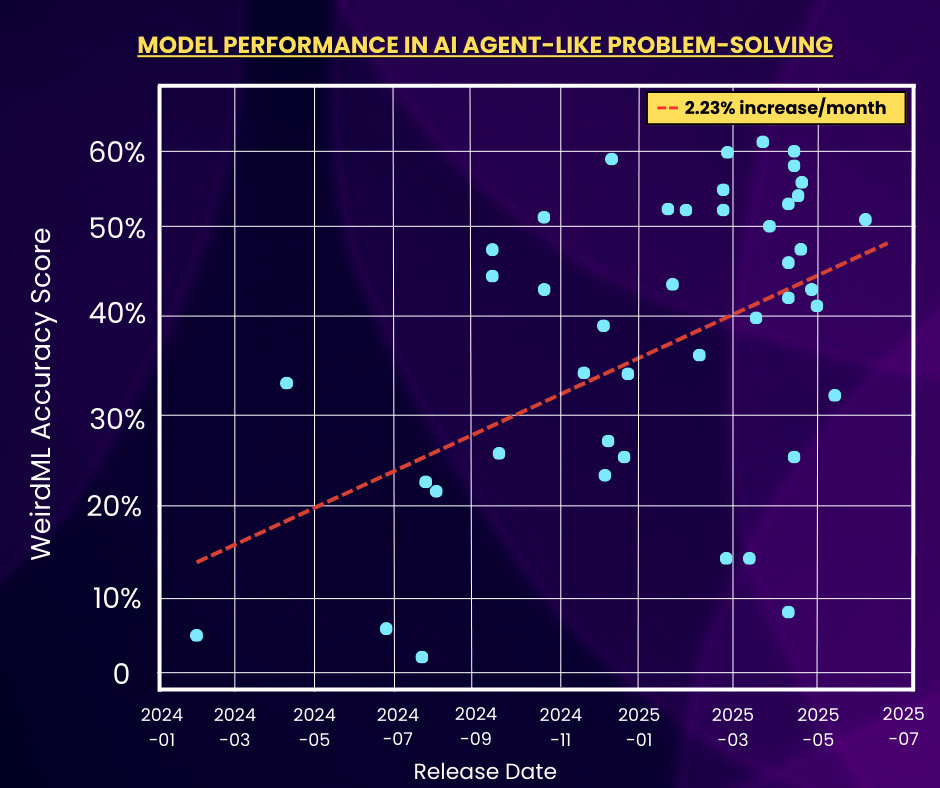
Here, “agent-like problem-solving” is measured using WeirdML score, a metric in Epoch AI’s Benchmarking Hub that measures a model’s ability to perform iterative, feedback-driven problem-solving on unusual ML tasks that require agent-like versatility. From the scatter plot above, over the past year and a half, accuracy on average has increased considerably by over 2% per month. This growth is a core reason for the rapid advancement of next-gen AI agents such as Vengo AI, as the models behind these agents are progressing significantly in terms of agent-like capability and problem-solving versatility.
Final Thoughts
Over the past decade-plus, AI models have transformed from a niche tool to a ubiquitous asset in everyday life, and the graphs above depict why. They have scaled by several orders of magnitude in terms of computational power, size, efficiency, and performance – transcending the boundaries of technology and redefining the possibilities of AI. As efficiency and scale continue to advance, AI models will only become more and more essential, raising the question of how close (or how far away) we are from the arrival of AGI.
Datasets
https://epoch.ai/data/ai-models?view=table

